Is Agriculture Non-Woven Fabric Eco-Friendly?
As the world moves toward more sustainable practices, industries across the globe are exploring eco-friendly materials. Agriculture is no exception, with many farmers and agricultural suppliers turning to non-woven fabric for a variety of purposes. But is this material truly eco-friendly? In this post, we will explore the environmental benefits and potential drawbacks of agriculture non-woven fabric to help you make an informed decision.
What is Agriculture Non-Woven Fabric?
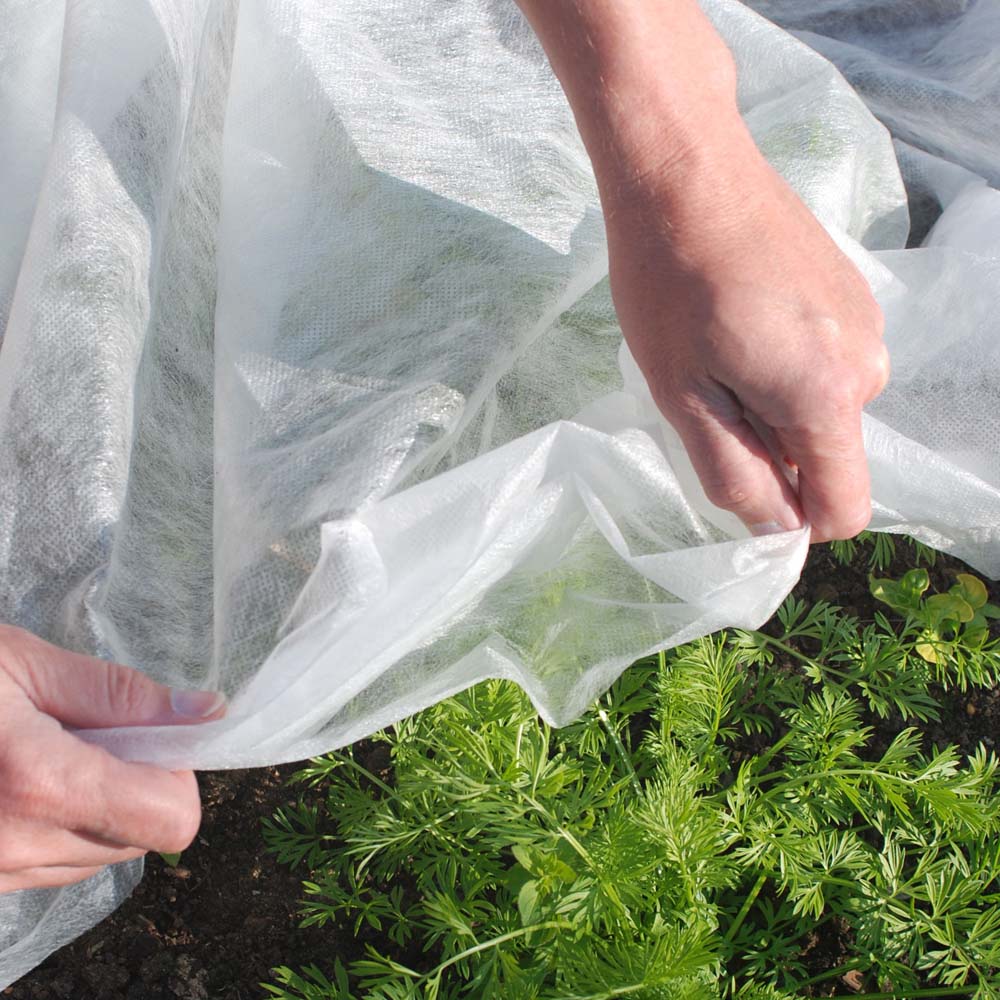
It is a versatile material widely used in farming and gardening. Made from synthetic fibers like polypropylene, it is created through a process that bonds fibers together without the need for weaving or knitting. This fabric is commonly used in agricultural applications such as crop protection, weed control, and soil erosion prevention.
Environmental Benefits of Agriculture Non-Woven Fabric
Non-woven fabric has gained popularity in agriculture due to its numerous environmental advantages:
- Breathable and Lightweight
Unlike plastic sheeting or traditional covers, agriculture non-woven fabric is breathable. This allows moisture and air to pass through, promoting healthy plant growth. Its lightweight nature reduces the need for heavy equipment, cutting down on energy consumption and soil compaction. - Biodegradable Options
While many non-woven fabrics are made from synthetic materials, there are biodegradable versions available. These fabrics decompose naturally over time, reducing the long-term environmental impact. Biodegradable non-woven fabric is especially beneficial for farmers looking to minimize waste. - Water Conservation
Non-woven fabric helps conserve water by reducing evaporation and retaining moisture in the soil. By keeping the soil consistently moist, plants require less frequent irrigation, leading to significant water savings. This can be particularly important in regions facing water scarcity. - Weed Control Without Chemicals
One of the most significant advantages of agriculture non-woven fabric is its ability to suppress weeds without the need for harmful chemical herbicides. By blocking sunlight, it prevents weed seeds from germinating, providing a natural alternative to chemical weed control methods.
Potential Environmental Concerns
While it is offers many eco-friendly benefits, there are some concerns that need to be addressed:
- Non-Biodegradable Options
Not all non-woven fabrics are biodegradable. Some products, particularly those made from polypropylene, can take hundreds of years to break down. This raises concerns about the accumulation of non-degradable materials in the environment, especially if the fabric is not properly disposed of after use. - Single-Use Products
Many agricultural non-woven fabrics are used for one season and then discarded. The disposable nature of these fabrics can lead to large amounts of waste if not properly recycled or reused. This can contribute to pollution and landfill overflow. - Production Energy Consumption
The production of synthetic non-woven fabric requires energy, which can contribute to carbon emissions, especially if the fabric is made from non-renewable resources. However, the environmental impact of production can vary depending on the manufacturing process.
How Can We Make Agriculture Non-Woven Fabric More Eco-Friendly?
To enhance the sustainability of the products, several measures can be taken:
- Opt for Biodegradable Materials
Choosing biodegradable or eco-friendly non-woven fabrics made from plant-based materials can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. These fabrics break down naturally and do not contribute to long-term pollution. - Improve Recycling and Reuse Practices
Encouraging the recycling of non-woven fabric can help minimize its environmental impact. Some manufacturers are developing programs that allow farmers to return used fabric for recycling. Additionally, using the fabric for multiple growing seasons can help reduce waste. - Choose Sustainable Manufacturing
Selecting non-woven fabrics made with sustainable manufacturing processes can also reduce the environmental impact. Look for fabrics produced using renewable energy sources or those that have a smaller carbon footprint.
Conclusion
Agriculture non-woven fabric can be an eco-friendly option when used correctly, offering benefits such as water conservation, weed control without chemicals, and biodegradable alternatives. However, it is crucial to choose fabrics that are made from sustainable materials and to ensure proper disposal or recycling practices are followed. By making informed decisions and opting for more eco-conscious choices, the agricultural industry can continue to benefit from non-woven fabrics while minimizing its environmental impact.
Ultimately, it can play an important role in promoting sustainability in farming — but only if it is used responsibly and in conjunction with other green practices.